on
Linker Scripts for MSP430G2553
This post will expain some words used in linker scripts of msp430g2553. The following is an illustration of linking operation:
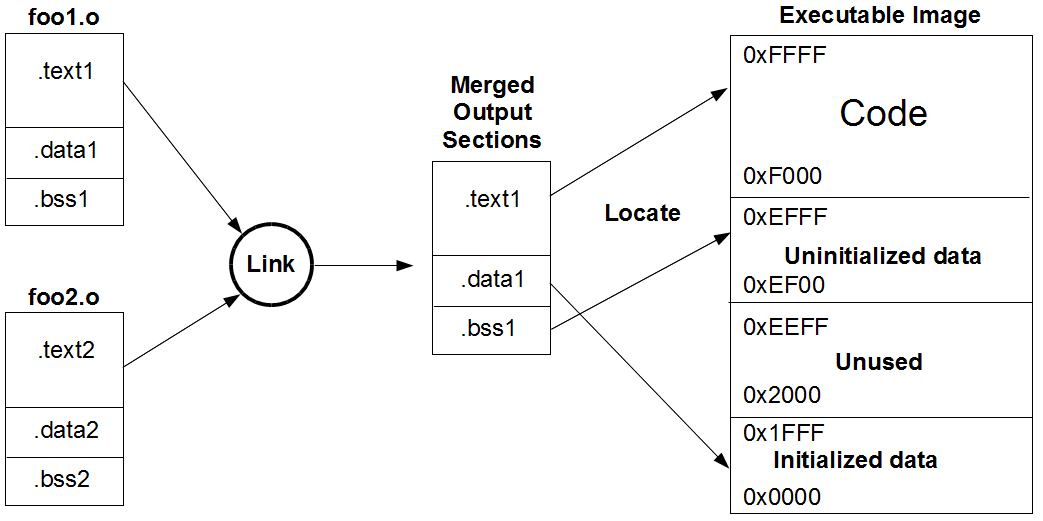
First of all, we will dissect the first line in the linker script.
ENTRY(_start)
This defines the entry point into the chip. On exit from a reset condition, the first thing that the MCU executes is at _start. To view this section (_start) please find in the linker script.
The linker script then defines the sections of the memory map that in to which it will map the various sections of the object files. It does this in Memory section.
MEMORY {
SFR : ORIGIN = 0x0000, LENGTH = 0x0010 /* END=0x0010, size 16 */
RAM : ORIGIN = 0x0200, LENGTH = 0x0200 /* END=0x03FF, size 512 */
INFOMEM : ORIGIN = 0x1000, LENGTH = 0x0100 /* END=0x10FF, size 256 as 4 64-byte segments */
INFOA : ORIGIN = 0x10C0, LENGTH = 0x0040 /* END=0x10FF, size 64 */
INFOB : ORIGIN = 0x1080, LENGTH = 0x0040 /* END=0x10BF, size 64 */
INFOC : ORIGIN = 0x1040, LENGTH = 0x0040 /* END=0x107F, size 64 */
INFOD : ORIGIN = 0x1000, LENGTH = 0x0040 /* END=0x103F, size 64 */
ROM (rx) : ORIGIN = 0xC000, LENGTH = 0x3FDE /* END=0xFFDD, size 16350 */
BSLSIGNATURE : ORIGIN = 0xFFDE, LENGTH = 0x0002
VECT1 : ORIGIN = 0xFFE0, LENGTH = 0x0002
VECT2 : ORIGIN = 0xFFE2, LENGTH = 0x0002
VECT3 : ORIGIN = 0xFFE4, LENGTH = 0x0002
VECT4 : ORIGIN = 0xFFE6, LENGTH = 0x0002
VECT5 : ORIGIN = 0xFFE8, LENGTH = 0x0002
VECT6 : ORIGIN = 0xFFEA, LENGTH = 0x0002
VECT7 : ORIGIN = 0xFFEC, LENGTH = 0x0002
VECT8 : ORIGIN = 0xFFEE, LENGTH = 0x0002
VECT9 : ORIGIN = 0xFFF0, LENGTH = 0x0002
VECT10 : ORIGIN = 0xFFF2, LENGTH = 0x0002
VECT11 : ORIGIN = 0xFFF4, LENGTH = 0x0002
VECT12 : ORIGIN = 0xFFF6, LENGTH = 0x0002
VECT13 : ORIGIN = 0xFFF8, LENGTH = 0x0002
VECT14 : ORIGIN = 0xFFFA, LENGTH = 0x0002
VECT15 : ORIGIN = 0xFFFC, LENGTH = 0x0002
RESETVEC : ORIGIN = 0xFFFE, LENGTH = 0x0002
}
It shows that the Flash memory (ROM) section starts at address 0xC000 and is 15KB long or 15,360 bytes long which in hex is 0x3FDE. The RAM memory section starts a address 0x20000000 and is 8KB long or 8192 bytes long, which in hex is 0x02000 . All of this information is provided to the linker via the memory section of the linker script. Also note the the ROM memory s defined as (rx) which means that it has read and execute only, whereas the RAM memory is defined as (xrw) which means that it is read, write and execute.
The next major section of the linker script is called SECTIONS. It defines where each if the various sections of the object files goes into the memory map defined in the MEMORY section.
SECTIONS
{
.bslsignature : {} > BSLSIGNATURE
__interrupt_vector_1 : { KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_1 )) KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_trapint)) } > VECT1
__interrupt_vector_2 : { KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_2 )) } > VECT2
__interrupt_vector_3 : { KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_3 )) KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_port1)) } > VECT3
__interrupt_vector_4 : { KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_4 )) KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_port2)) } > VECT4
__interrupt_vector_5 : { KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_5 )) } > VECT5
__interrupt_vector_6 : { KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_6 )) KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_adc10)) } > VECT6
__interrupt_vector_7 : { KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_7 )) KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_usciab0tx)) } > VECT7
__interrupt_vector_8 : { KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_8 )) KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_usciab0rx)) } > VECT8
__interrupt_vector_9 : { KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_9 )) KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_timer0_a1)) } > VECT9
__interrupt_vector_10 : { KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_10)) KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_timer0_a0)) } > VECT10
__interrupt_vector_11 : { KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_11)) KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_wdt)) } > VECT11
__interrupt_vector_12 : { KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_12)) KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_comparatora)) } > VECT12
__interrupt_vector_13 : { KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_13)) KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_timer1_a1)) } > VECT13
__interrupt_vector_14 : { KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_14)) KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_timer1_a0)) } > VECT14
__interrupt_vector_15 : { KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_15)) KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_nmi)) } > VECT15
__reset_vector :
{
KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_16))
KEEP (*(__interrupt_vector_reset))
KEEP (*(.resetvec))
} > RESETVEC
.......
The first section defined under SECTIONS is the __interrupt_vector_{VECTOR_NUMBER} section. This section contains the interrupt vector table and reset vector i.e. the body of the interrupt vector 1 routine specified stored at an address 0xFFE0 with 2 width bytes (from 0xFFE0 to 0xFFE1).
......
.rodata :
{
. = ALIGN(2);
*(.plt)
*(.rodata .rodata.* .gnu.linkonce.r.* .const .const:*)
*(.rodata1)
KEEP (*(.gcc_except_table)) *(.gcc_except_table.*)
PROVIDE (__preinit_array_start = .);
KEEP (*(.preinit_array))
PROVIDE (__preinit_array_end = .);
PROVIDE (__init_array_start = .);
KEEP (*(SORT(.init_array.*)))
KEEP (*(.init_array))
PROVIDE (__init_array_end = .);
PROVIDE (__fini_array_start = .);
KEEP (*(.fini_array))
KEEP (*(SORT(.fini_array.*)))
PROVIDE (__fini_array_end = .);
} > ROM
.......
The ALIGN(2) instructions tells the linker that this section ought to be word aligned. Since this is a 16-bit machine it typically needs to be word aligned (16-bit -> 2 bytes hence the ‘2’ specified with the align command. )
Output Section Description
The full description of an output section looks like this:
section [address] [(type)] : [AT(lma)]
{
output-section-command
output-section-command
...
} [>region] [AT>lma_region] [:phdr :phdr …] [=fillexp]
Output sections
.text: Opcodes generated by the compiler are stored in this section..bss, .data: The static data region is actually subdivided into two further sections:- one for uninitialized-definitions (int var1;).
- one for initialised-definitions (int var2 = 10;) So it would not be unexpected for the address of var1 and var2 to not be adjacent to each other in memory. The uninitialized-definitions’ section is commonly known as the .bss or ZI section. The initialised-definitions’ section is commonly known as the .data or RW section.
.rodata: specifically for constant values. This section can be placed (in ROM) separate from the .data section.- Automatic vairable (.stack) The majority of variables are defined within functions and classed as automatic variables. This also includes parameters and any temporary-returned-object (TRO) from a non-void function. The default model in general programming is that the memory for these program objects is allocated from the stack. For parameters and TRO’s the memory is normally allocated by the calling function (by pushing values onto the stack), whereas for local objects, memory is allocated once the function is called. This key feature enables a function to call itself – recursion (though recursion is generally a bad idea in embedded programming as it may cause stack-overflow problems). In this model, automatic memory is reclaimed by popping the stack on function exit. It is important to note that the compiler does NOT create a .stack segment. Instead, opcodes are generated that access memory relative to some register, the Stack Pointer, which is configured at program start-up to point to the top of the stack segment (see below) However, on most modern microcontrollers, especially 32-bit RISC architectures, automatics are stored in scratch registers, where possible, rather than the stack. For example the ARM Architecture Procedure Call Standard (AAPCS) defines which CPU registers are used for function call arguments into, and results from, a function and local variables.
- Dynamic data (.heap) Memory for dynamic objects is allocated from a section known as the Heap. As with the Stack, the Heap is not allocated by the compiler at compile time but by the Linker at link-time.
Simple Linker Script Commands
-
ENTRY(symbol)The first instruction to execute in a program is called the entry point. You can use the ENTRY linker script command to set the entry point.
-
OUTPUT_ARCH(bfdarch)Specify a particular output machine architecture. You can see the architecture of an object file by using the objdump program with the -f option.
-
ASSERT(exp, message)Ensure that exp is non-zero. If it is zero, then exit the linker with an error code, and print message.
Assigning Values to Symbols
-
In some cases, it is desirable for a linker script to define a symbol only if it is referenced and is not defined by any object included in the link. For example, traditional linkers defined the symbol etext. However, ANSI C requires that the user be able to use etext as a function name without encountering an error. The PROVIDE keyword may be used to define a symbol, such as etext, only if it is referenced but not defined. The syntax is PROVIDE(symbol = expression). Here is an example of using PROVIDE to define etext: ```Makefile SECTIONS { .text : { *(.text) _etext = .; PROVIDE(etext = .); } }In this example, if the program defines _etext (with a leading underscore), the linker will give a multiple definition error. If, on the other hand, the program defines etext (with no leading underscore), the linker will silently use the definition in the program. If the program references etext but does not define it, the linker will use the definition in the linker script.
-
KEEPWhen link-time garbage collection is in use (-gc-sections), it is often useful to mark sections that should not be eliminated. This is accomplished by surrounding an input section’s wildcard entry with KEEP()
Builtin Functions
-
ABSOLUTE(exp)Return the absolute (non-relocatable, as opposed to non-negative) value of the expression exp. Primarily useful to assign an absolute value to a symbol within a section definition, where symbol values are normally section relative.
-
Return the absolute address (the VMA) of the named section. Your script must previously have defined the location of that section. In the following example, symbol_1 and symbol_2 are assigned identical values: ```Makefile SECTIONS { ... .output1 : { start_of_output_1 = ABSOLUTE(.); … } .output : { symbol_1 = ADDR(.output1); symbol_2 = start_of_output_1; } } ...
Reference
- Linker Command Language - Reference for concept or syntax.
- Using ld, the Gnu Linker