on
Compilation process of a msp430g2553 project
The compiler is responsible for allocating memory for definitions (static and automatic) and generating opcodes from program statements. A relocatable object file (.o) is produced. The assembler also produces .o files from assembly-language source.
Understanding the compilation process is helpful for us to analyze and detect the problem with ease in compilation process.
The compilation process is the important things for a beginner in microcontroller programming. Some people don’t understand it with clarify, that results in they can’t fix a problem from the compiling time.
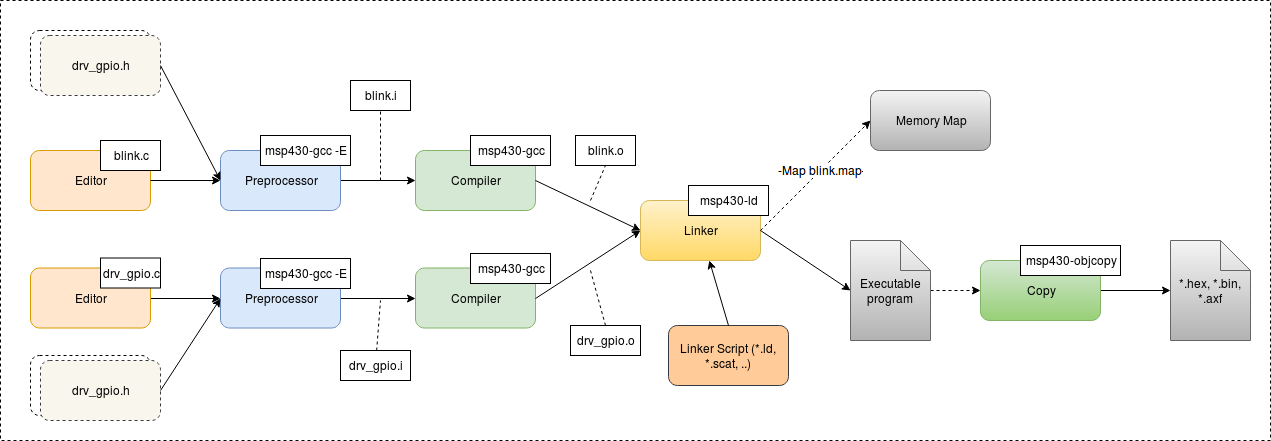
The above figure illustrate the compilation process of a simple blinky program.
.
├── blink.c
├── drv_gpio.c
└── drv_gpio.h
The following is the blink.c program:
#include <msp430g2553.h>
void main(void)
{
WDTCTL = WDTPW | WDTHOLD; /* Stop watchdog timer */
P1DIR |= 0x40; /* Set P1.6 to output direction */
for(;;)
{
P1OUT ^= 0x40; /* Toggle P1.6 using exclusive-OR */
/* Wait for 200000 cycles */
__delay_cycles(200000);
}
}
To compile the program, the compiler will prefrom the preprocessor stage by command msp430-gcc -E blink.c -o blink.i (The compiling options for the target are ignored, you only focus on the main command for the compilation process).
$ msp430-gcc -E blink.c -o blink.i
$ ll
total 24
drwxrwxr-x 2 nhivp nhivp 4096 Th07 22 16:59 ./
drwxrwxr-x 4 nhivp nhivp 4096 Th07 22 15:24 ../
-rw-rw-r-- 1 nhivp nhivp 596 Th07 19 21:37 blink.c
-rw-rw-r-- 1 nhivp nhivp 8719 Th07 22 16:59 blink.i
The output is in the form of preprocessed source code, which is sent to the standard output. The following is the output of preprocessor stage.
# 1 "blink.c"
# 1 "<built-in>"
# 1 "<command-line>"
# 1 "blink.c"
......
void __nop (void);
void __dint (void);
void __eint (void);
unsigned int __read_status_register (void);
typedef unsigned int __istate_t;
......
void __watchdog_clear ();
# 5 "/usr/lib/gcc/msp430/4.6.3/../../../../msp430/include/in430.h" 2 3
# 113 "/usr/lib/gcc/msp430/4.6.3/../../../../msp430/include/msp430g2553.h" 2 3
# 135 "/usr/lib/gcc/msp430/4.6.3/../../../../msp430/include/msp430g2553.h" 3
extern volatile unsigned char IE1 __asm__("__" "IE1");
extern volatile unsigned char IFG1 __asm__("__" "IFG1");
extern volatile unsigned char IE2 __asm__("__" "IE2");
extern volatile unsigned char IFG2 __asm__("__" "IFG2");
# 172 "/usr/lib/gcc/msp430/4.6.3/../../../../msp430/include/msp430g2553.h" 3
extern volatile unsigned char ADC10DTC0 __asm__("__" "ADC10DTC0");
extern volatile unsigned char ADC10DTC1 __asm__("__" "ADC10DTC1");
......
# 8 "blink.c" 2
void main(void)
{
WDTCTL = (0x5A00) | (0x0080);
P1DIR |= 0x40;
for(;;)
{
P1OUT ^= 0x40;
__delay_cycles(200000);
}
}
The preprocessed output file is quite large. There are three things that preprocessor does:
-
It removes all the comments from our program blink.c
Before:
void main(void) { WDTCTL = WDTPW | WDTHOLD; /* Stop watchdog timer */ P1DIR |= 0x40; /* Set P1.6 to output direction */ for(;;) { P1OUT ^= 0x40; /* Toggle P1.6 using exclusive-OR */ /* Wait for 200000 cycles */ __delay_cycles(200000); } }After:
void main(void) { WDTCTL = (0x5A00) | (0x0080); P1DIR |= 0x40; for(;;) { P1OUT ^= 0x40; __delay_cycles(200000); } } -
It includes code from header and source file
You can see the header files (
msp430g2553.h,iomacros.handintrinsics.h) included into the preprocessed file (blink.i). -
It replaces macros (if there are any that are used in the program) with code.
Before:
... #define IE1_ 0x0000 /* Interrupt Enable 1 */ ... WDTCTL = WDTPW | WDTHOLD; /* Stop watchdog timer */ ...After the preprocessor stage, the macro
WDTPWis replaced by0x5A00.... extern volatile unsigned char IE1 __asm__("__" "IE1"); ... WDTCTL = (0x5A00) | (0x0080); ...
The error often occur in this stage will be ```No such file or directory`` when the include header files are not found.
Error doesn’t occur in case the header files which consist of some used macros are not included. For example, the blinky program didn’t include the header file msp430g2553.h. And below is result:
# 1 "blink.c"
# 1 "<built-in>"
# 1 "<command-line>"
# 1 "blink.c"
# 9 "blink.c"
void main(void)
{
WDTCTL = WDTPW | WDTHOLD;
P1DIR |= 0x40;
for(;;)
{
P1OUT ^= 0x40;
__delay_cycles(200000);
}
}
After passing the preprocessor stage, the compiler will compile the source code (blink.i) into objects file (blink.o). The object file contains the compiled source code – opcodes and data sections. Note that the object file only contains the sections for static variables. At this stage, section locations are not fixed.
$ msp430-gcc -c blink.i -o blink.o
$ ll
total 28
drwxrwxr-x 2 nhivp nhivp 4096 Th07 22 18:32 ./
drwxrwxr-x 4 nhivp nhivp 4096 Th07 22 15:24 ../
-rw-rw-r-- 1 nhivp nhivp 596 Th07 22 18:30 blink.c
-rw-rw-r-- 1 nhivp nhivp 8719 Th07 22 18:30 blink.i
-rw-rw-r-- 1 nhivp nhivp 788 Th07 22 18:32 blink.o
From this stage, you can get error (if any) such as syntax of C, lack of header files, …
With multiple object files, we will link them by using the msp430-ld with a linker script. You can find the linker scripts in the support files. It consists of the msp430g2553.ld and msp430g2553_symbols.ld.
In the linking stage, we often get some errors like:
- Multiple definition a funtion or variable. This error will occur when linking all objects file into a executable file.
- Lack of linker script.
To investigate compilation process with more source code such as assembly code, library, … You can read more at link or this.